What's MIOS?
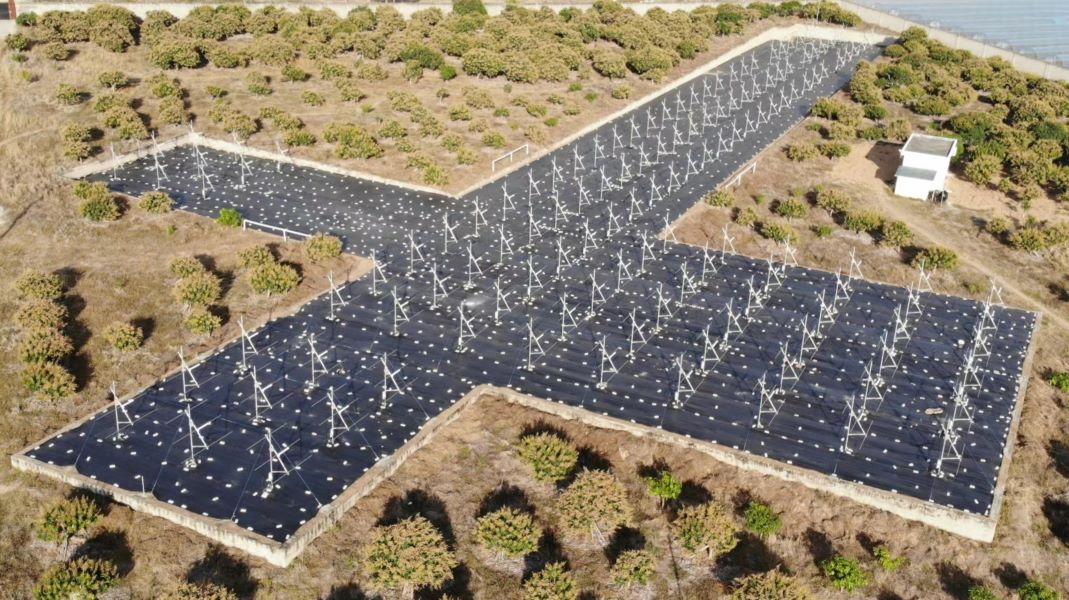
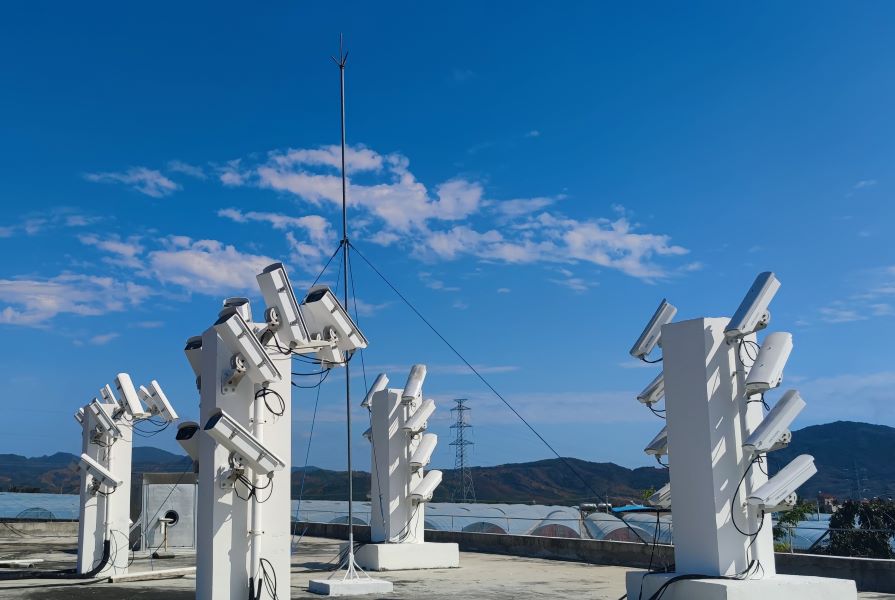
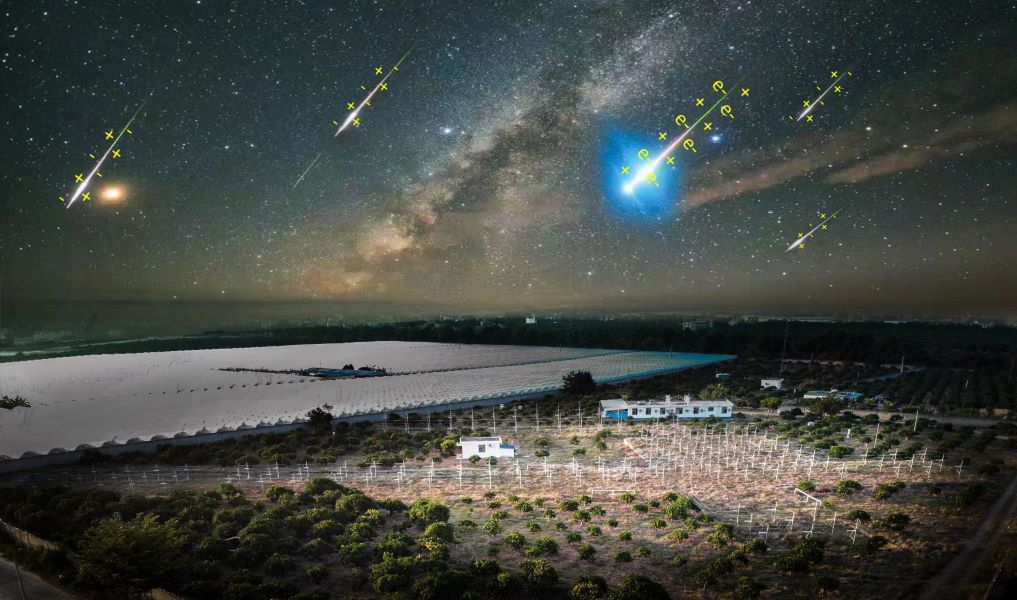
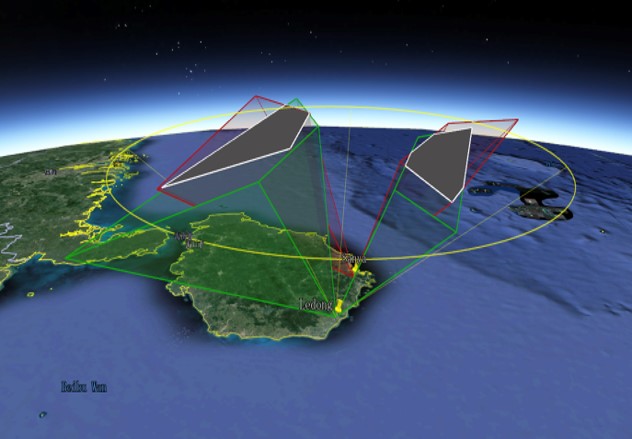
Meteoroids entering the Earth's atmosphere significantly disturb the background ionosphere, producing ionized columns and plasma density irregularities, change the ionospheric composition, and even seed large-scale ionospheric irregularity structures. However, due to the limitations of previous measurements, some physical processes, for example, how efficiently various meteoroids affect the background ionosphere, either producing or not producing some specific meteor trail irregularity phenomena, and the related meteoroid properties and origins, are less well understood. Under the support of national natural science foundation of China, a Meteor and ionospheric Irregularity Observation System (MIOS) was designed to simultaneously capture the radar and optical signatures of meteors and plasma density irregularities. MIOS consists of multistation optical subsystem at Ledong (18.4°N, 109°E) and Sanya (18.3°N, 109.6°E), and radar subsystem including a 38.9 MHz all-sky interferometric radar and a 47.5 MHz coherent phased array radar at Ledong, has been in full operational since December 2021. It is expected that the MIOS will provide an important tool to study the generation and evolution of various meteor trail irregularities and the properties of the corresponding meteoroids.
Bright meteor events
MIOS activities
Nov. 2022 – We finished the technical test of MIOS.
Oct. 2021 – We finished the setup of the antenna array of MIOS radar subsystem.
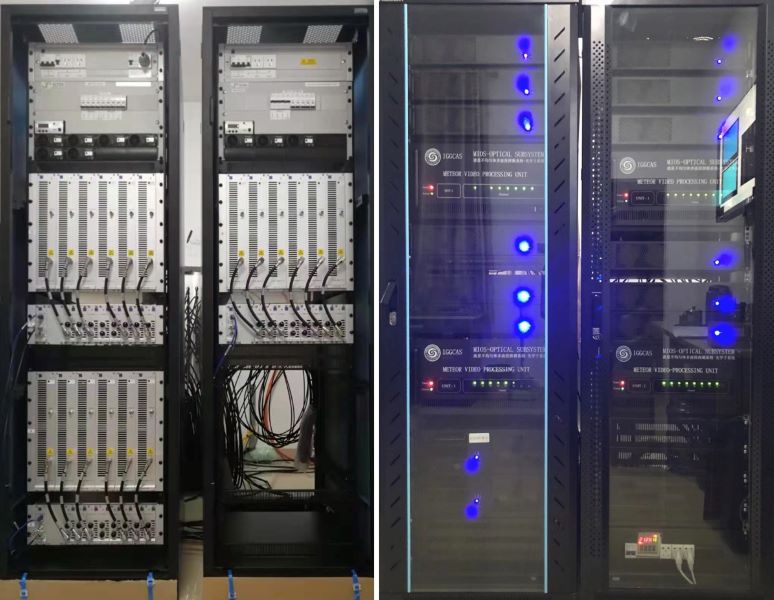
Aug. 2021 – A near-real-time-display software was developed for MIOS optical subsystem (please see the Data page).
Feb. 2021 – A near-real-time-display software was developed for MIOS radar subsystem (please see the Data page).
Nov. 2020 – A sub array of MIOS radar narrow beam subsystem was installed at Ledong, being operated for routine observation of meteor and ionospheric irregularity.
Oct. 2020 – The FOV of MIOS optical subsystem was enlarged. Optical meteors from both the southern and northern sky of Sanya/Ledong can be detected.
Dec. 2019 – The MIOS optical subsystem was developed, being operated for routine observation of optical meteors.
June 2019 – We leveled the site for the installation of antenna array of the MIOS radar narrow beam subsystem.
Dec. 2018 – The code for deriving meteor orbital parameters and spectra from video observations was developed.
Aug. 2018 – The MIOS radar wide beam subsystem was installed at Ledong, being operated for routine observation of specular and nonspecular meteors.
Jan. 2018 – We finished the design of MIOS, which consists of the optical subsystem (will be installed at Ledong and Sanya) and the radar wide beam and narrow beam subsystem (will be installed at Ledong).
Dec. 2017 – Several video cameras were installed at Sanya and Ledong for testing common volume observations.
Aug. 2017 – The MIOS project was approved by NSF of China.